Was ist ein KI-Bild? Ihr umfassender Leitfaden zum Verständnis KI-generierter Bilder
Zuletzt aktualisiert: 2026-01-22 18:07:43

Das Wichtigste in Kürze
Ein KI-Bild bezeichnet eine durch Algorithmen der künstlichen Intelligenz erzeugte digitale Grafik, die üblicherweise auf Basis von Textbeschreibungen (Prompts) oder bestehenden Bildvorlagen entsteht. Anders als klassische Fotografien oder von Menschen geschaffene Kunstwerke werden diese Visualisierungen durch Machine-Learning-Modelle synthetisiert, die auf Millionen von Datensätzen trainiert wurden. Dank leistungsstarker Modelle wie DALL-E-3, Midjourney und Stable Diffusion lassen sich so in Sekundenschnelle fotorealistische Bilder, Illustrationen und künstlerische Werke direkt aus Ihren individuellen Beschreibungen generieren.
Wesentliche Merkmale:
- Anstatt manuell gezeichnet oder fotografisch erfasst zu werden, entstehen diese Bilder rein algorithmisch auf Basis komplexer Datenmuster.
- Die Erstellung basiert auf der intelligenten Verknüpfung von Informationen anstatt auf klassischem, zeitintensivem Pixel-Design.
- Professionelle Ergebnisse werden in Sekundenschnelle geliefert, was den oft tagelangen Aufwand herkömmlicher Methoden drastisch verkürzt.
- Zudem lassen sich verschiedenste Stile und Konzepte frei kombinieren, um visuelle Welten jenseits der Realität zu erschaffen.
Vielseitige Einsatzmöglichkeiten: Die Anwendungsbereiche reichen von professionellen Marketing-Grafiken und Social-Media-Inhalten über Concept Art und Produkt-Mockups bis hin zu hochwertigen Lehrmaterialien sowie der freien kreativen Entfaltung.
Ein umfassender Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren von Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026 sowie eine detaillierte Analyse ihrer jeweiligen Preisstrategien.
Detaillierter Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026: Ein umfassender Einblick in Funktionen und Preismodelle.Ein umfassender Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren von Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026 sowie eine detaillierte Analyse ihrer jeweiligen Preisstrategien.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- KI-Bilder verstehen: Die wichtigsten Grundlagen
- Funktionsweise und Technologie der KI-Bildgenerierung
- Beliebte KI-Bildgeneratoren im direkten Vergleich
- In wenigen Schritten zum ersten eigenen KI-Bild
- So identifizieren Sie KI-generierte Bilder zuverlässig
- Praxisnahe Einsatzmöglichkeiten und Anwendungsbeispiele
- Technologische Grenzen und aktuelle Herausforderungen
- Häufig gestellte Fragen (FAQ)
Ein umfassender Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren von Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026 sowie eine detaillierte Analyse ihrer jeweiligen Preisstrategien.
Detaillierter Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026: Ein umfassender Einblick in Funktionen und Preismodelle.Ein umfassender Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren von Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026 sowie eine detaillierte Analyse ihrer jeweiligen Preisstrategien.
KI-Bilder verstehen: Die wichtigsten Grundlagen im Überblick
Als ich Anfang 2022 zum ersten Mal mit KI-generierten Bildern in Berührung kam, war meine Skepsis groß – zu unwahrscheinlich schien es, dass ein Computer Werke von handgemalter oder professionell fotografierter Qualität erschaffen könnte. Mittlerweile blicke ich jedoch auf zwei Jahre intensiver Erprobung und tausende generierte Bilder für verschiedenste Projekte zurück, wodurch ich ein fundiertes Verständnis sowohl für die beeindruckenden Möglichkeiten als auch für die bestehenden Limitationen dieser Technologie gewonnen habe.
Was zeichnet ein KI-generiertes Bild aus?
Der entscheidende Unterschied liegt im eigentlichen Entstehungsprozess, wobei sich bei herkömmlichen Bildern grundlegend drei Ursprünge differenzieren lassen:
In der Fotografie wird Licht aus der physischen Welt mittels Kamerasensoren eingefangen, wodurch Aufnahmen wie die eines Sonnenuntergangs erst durch das einzigartige Zusammenspiel von Licht, Wolken und Landschaft in einem exakt definierten Moment entstehen.
Im Bereich der digitalen Kunst erfolgt die Gestaltung manuell durch Künstler mittels Software wie Photoshop oder Procreate, wobei jeder Pinselstrich sowie sämtliche Farb- und Kompositionsentscheidungen unmittelbar aus menschlicher Intention hervorgehen.
Die KI-Bildgenerierung basiert auf einem völlig neuen Prinzip, bei dem Bilder mithilfe mathematischer Modelle entstehen, die zuvor Millionen existierender Aufnahmen analysiert haben. Anstatt bei einer Eingabe wie „eine Katze mit Astronautenhelm auf dem Mars“ lediglich nach einer Vorlage zu suchen, synthetisiert das System ein gänzlich neues Werk aus erlernten Mustern von Katzen, Helmen und Mars-Landschaften sowie grafischen Gestaltungsprinzipien.
Man kann es sich so vorstellen: Während traditionelle Kunst dem Kochen nach einem eigenen Rezept gleicht, ist die KI-Generierung eher mit der Beschreibung eines Gerichts gegenüber einem Experten vergleichbar, der dank seines Wissens aus unzähligen Geschmackserlebnissen in der Lage ist, jedes Aroma allein aus der Erinnerung heraus perfekt zu rekonstruieren.
Ein kurzer Rückblick: Wissenswertes zur bisherigen Entwicklung
Die KI-Bildgenerierung hat sich keineswegs über Nacht entwickelt; vielmehr ist das Verständnis dieser technologischen Evolution entscheidend, um den heutigen Stand der Technik vollumfänglich einordnen zu können:
1960er–1990er: Frühe Experimente wie Harold Cohens AARON-System nutzten regelbasierte Programmierung zur Erstellung einfacher Zeichnungen, wobei es sich dabei eher um algorithmische Kunst als um echte Künstliche Intelligenz handelte.
2014: Mit dem Aufkommen der Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) entstanden erstmals wahrhaft überzeugende KI-generierte Gesichter und Bilder, wenngleich die Resultate damals noch limitiert waren und umfassendes technisches Fachwissen erforderten.
2021–2022: Der entscheidende technologische Durchbruch gelang durch die Einführung von Diffusionsmodellen und Transformer-Architekturen, wodurch Tools wie DALL E von OpenAI, Stable Diffusion von Stability AI und Midjourney die hochwertige Bildgenerierung plötzlich für ein breites Publikum zugänglich machten.
2023–2025: In dieser Phase rasanter technologischer Reifung haben Modelle gelernt, selbst komplexe Prompts präzise umzusetzen und Textelemente nahtlos in Bilder zu integrieren. Neben einer deutlich gesteigerten Konsistenz wurden dabei auch typische Artefakte, wie etwa die fehlerhafte Darstellung von Händen, erfolgreich eliminiert.
Laut aktuellen Analysen von Grand View Research belief sich der Marktwert von KI-Bildgeneratoren im Jahr 2022 auf 299,2 Millionen US-Dollar und soll bis 2030 mit einer durchschnittlichen jährlichen Wachstumsrate von 17,2 % expandieren, was die rasant zunehmende Akzeptanz dieser Technologie in verschiedensten Branchen verdeutlicht.
Ein umfassender Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren von Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026 sowie eine detaillierte Analyse ihrer jeweiligen Preisstrategien.
Detaillierter Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026: Ein umfassender Einblick in Funktionen und Preismodelle.Ein umfassender Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren von Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026 sowie eine detaillierte Analyse ihrer jeweiligen Preisstrategien.
So funktioniert die Technologie hinter KI-generierten Bildern
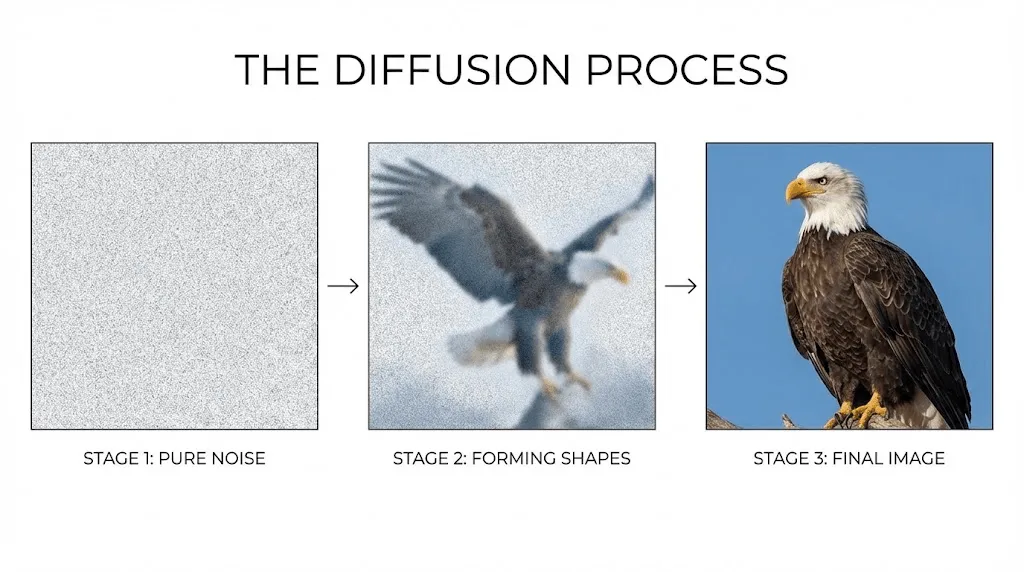
Obwohl für die Bedienung dieser Tools kein Informatikstudium erforderlich ist, erzielen Sie durch ein grundlegendes Verständnis der Technologie deutlich bessere Ergebnisse; erfahren Sie hier, was bei der Generierung eines KI-Bildes hinter den Kulissen geschieht.
Die Grundlagen des Modelltrainings
Bevor ein KI-Modell in der Lage ist, eigenständig Bilder zu generieren, durchläuft es einen umfassenden und intensiven Trainingsprozess:
- Datenerfassung: Die Grundlage bilden Modelle, die an gewaltigen Datensätzen aus Millionen oder Milliarden von Bild-Text-Paaren trainiert werden, wobei die oft aus dem Internet stammenden Quelldaten rechtliche Fragen zum Urheberrecht aufwerfen, auf die wir später noch detailliert eingehen.
- Mustererkennung: Durch die stetige Analyse lernt das System die Korrelationen zwischen Sprache und visuellen Elementen, sodass es versteht, dass ein „Sonnenuntergang“ typischerweise Orange- und Purpurtöne umfasst, während „professionelle Porträts“ oder „Aquarellmalereien“ durch jeweils ganz spezifische Anforderungen an Lichtsetzung, Komposition und Textur definiert sind.
- Mathematische Kodierung: Da das Modell keine physischen Bilder speichert, sondern mathematische Repräsentationen visueller Konzepte entwickelt, erlernt es eher die zugrundeliegende „Grammatik“ der Bildsprache, anstatt lediglich konkrete Beispiele auswendig zu lernen.
Die Trainingsphase kann auf leistungsstarken Computer-Clustern mehrere Wochen in Anspruch nehmen und verursacht Kosten in Millionenhöhe, weshalb etablierte Branchengrößen wie OpenAI, Stability AI und Google dieses Technologiefeld heute maßgeblich dominieren.
Die drei wichtigsten Technologien im Überblick
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
Zwischen 2014 und 2021 bildeten GANs die technologische Basis der meisten KI-Bildgeneratoren, wobei das System auf dem Zusammenspiel zweier miteinander konkurrierender neuronaler Netzwerke basiert:
- Der Generator erzeugt Bildmaterial mit dem Ziel, sein technologisches Gegenstück durch täuschend echte Resultate zu überlisten
- Der Diskriminator evaluiert diese Ergebnisse wiederum kritisch, um Fälschungen zuverlässig zu identifizieren
Dieser kompetitive Prozess sorgt für eine stetige Weiterentwicklung, bei der der Generator immer authentischere Bilder erschafft, während der Diskriminator lernt, Unstimmigkeiten präziser zu identifizieren. Trotz dieser Fortschritte weisen GANs oft Defizite in der Diversität und Stabilität auf, was sich häufig in monotonen Ergebnissen oder unvorhersehbaren Fehlern während des Trainings äußert.
Diffusionsmodelle (Der aktuelle Branchenstandard)
Moderne KI-Anwendungen wie DALL-E-3, Midjourney und Stable Diffusion basieren auf Diffusionsmodellen, die ihre Ergebnisse mithilfe eines faszinierenden Umkehrprozesses generieren:
- Der Prozess beginnt mit einem Feld aus reinem Bildrauschen, das aus einer Ansammlung zufälliger Pixel besteht.
- Gesteuert durch Ihren Text-Prompt reduziert das Modell diese Statik schrittweise, um die gewünschten Inhalte freizulegen.
- Über zahlreiche Iterationen hinweg kristallisieren sich so sukzessive erkennbare Strukturen und Merkmale heraus.
- Im letzten Schritt werden diese Details schließlich zu einem präzisen und kohärenten Gesamtbild zusammengeführt.
Ein passender Vergleich verdeutlicht diesen Prozess: Ähnlich wie ein Bildhauer aus einem Marmorblock Schritt für Schritt die verborgene Skulptur freilegt, transformiert die KI anfängliches visuelles Chaos gezielt in eine strukturierte, präzise Bildkomposition.
Im Vergleich zu herkömmlichen GANs bietet dieser Ansatz eine deutlich präzisere Kontrolle sowie eine höhere Konsistenz und Qualität, wobei die schrittweise Verfeinerung zudem innovative Möglichkeiten zur Bildanpassung direkt während des Generierungsprozesses eröffnet.
Transformer-basierte Modelle
DALL·E leistete Pionierarbeit, indem es die Bildgenerierung als sprachliche Herausforderung interpretierte und die bewährte Transformer-Architektur von ChatGPT adaptierte, um Pixel wie Wörter innerhalb eines visuellen Satzes zu verarbeiten.
Diese Architektur ist darauf spezialisiert, die komplexen Beziehungen zwischen verschiedenen Konzepten zu erfassen, sodass selbst vielschichtige Prompts – etwa ein „Renaissance-Gemälde eines Roboters beim Tee mit Marie Antoinette in einer Cyberpunk-Kulisse“ – präzise interpretiert und umgesetzt werden.
Vom Prompt zum Pixel: Was bei der Generierung tatsächlich passiert
Sobald Sie Ihren Prompt eingegeben und den Befehl zur Erstellung erteilt haben, lässt sich der dahinterstehende Prozess üblicherweise wie folgt beschreiben:
- Textkodierung: Ihr Prompt wird in numerische Vektoren übersetzt, um die semantische Bedeutung für die KI präzise interpretierbar zu machen.
- Navigation im latenten Raum: Das Modell durchsucht seinen mathematischen Wissensraum nach visuellen Konzepten, die Ihre Vorgaben exakt widerspiegeln.
- Iterative Verfeinerung: In einem mehrstufigen Prozess – bei Diffusionsmodellen meist 20 bis 50 Durchläufe – nimmt das Bild schrittweise Gestalt an und wird kontinuierlich präzisiert.
- Upscaling und Post-Processing: Ergänzende neuronale Netzwerke optimieren abschließend die Auflösung und arbeiten feinste Details für ein hochwertiges Ergebnis aus.
- Ausgabe: Das System liefert Ihnen das fertig generierte Bild in seiner finalen, einsatzbereiten Form.
Abhängig vom gewählten Modell, der gewünschten Auflösung und der aktuellen Systemauslastung nimmt dieser gesamte Prozess in der Regel lediglich 10 bis 60 Sekunden in Anspruch.
Ein umfassender Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren von Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026 sowie eine detaillierte Analyse ihrer jeweiligen Preisstrategien.
Detaillierter Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026: Ein umfassender Einblick in Funktionen und Preismodelle.Ein umfassender Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren von Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026 sowie eine detaillierte Analyse ihrer jeweiligen Preisstrategien.
Gängige KI-Bildgeneratoren im praxisnahen Vergleich
Nach einer intensiven Auseinandersetzung mit den einzelnen Plattformen zeige ich Ihnen hier die entscheidenden Unterschiede auf, die in der täglichen Praxis wirklich zählen.
Optionen für professionelle Ansprüche
MidjourneyIdeal für künstlerische und stilisierte Werke
- Zugang: Die Nutzung erfolgt primär über Discord, während eine dedizierte Web-Oberfläche bereits schrittweise eingeführt wird.
- Preisgestaltung: Die monatlichen Kosten variieren je nach Funktionsumfang zwischen 10 $ (Basic) und 60 $ (Mega).
- Stärken: Midjourney besticht durch eine konstant hohe ästhetische Qualität mit künstlerischer Note, wobei der Austausch innerhalb der Community das Erlernen effektiver Prompt-Strategien durch das Sichten fremder Kreationen erheblich erleichtert.
- Schwächen: Während das Discord-basierte Interface auf manche Nutzer unübersichtlich wirken kann, liegt eine weitere Einschränkung in der teils geringeren Präzision bei technischen Vorgaben oder extremem Fotorealismus im Vergleich zu Wettbewerbern.
- Ideal für: Kreativprofis und Illustratoren, die künstlerische Exzellenz über die strikte Einhaltung technischer Prompt-Vorgaben stellen.
Praxiserfahrung: Bei der Erstellung von Concept Art für ein Spieleprojekt lieferte Midjourney schneller als jede andere Anwendung unmittelbar einsetzbare Ergebnisse, die weniger wie bloße Zufallsprodukte, sondern vielmehr wie professionell gestaltete Designs wirkten.
DALL-E 3 (via ChatGPT) besticht durch eine besonders präzise und detailgetreue Interpretation komplexer Prompts.
- **Zugang & Kosten:** Der Zugriff erfolgt wahlweise über die API oder ein ChatGPT Plus-Abonnement für monatlich 20 $, welches bereits alle erweiterten Plattform-Funktionen umfasst.
- **Stärken:** Dank der nahtlosen ChatGPT-Integration lassen sich selbst hochkomplexe, nuancierte Prompts im natürlichen Dialog präzisieren, während ausgereifte Sicherheitsfilter für eine verlässliche Inhaltskontrolle sorgen.
- **Schwächen:** Die Ergebnisse wirken im Vergleich zu Midjourney oft sehr glatt und teils generisch; zudem können die geltenden Generierungslimits bei intensiver Nutzung einschränkend wirken.
- **Ideal für:** Geschäftsanwender und bestehende ChatGPT-Nutzer, die eine intuitive und präzise Text-zu-Bild-Umsetzung ohne kompliziertes Prompt Engineering suchen.
Erfahrungen aus der Praxis: Bei der Erstellung spezifischer Marketingmaterialien auf Basis detaillierter Markenrichtlinien überzeugt DALL-E-3 durch eine präzise Umsetzung, die im Vergleich zu anderen Tools deutlich weniger Korrekturschleifen erfordert.
Stable DiffusionIdeal für maximale Kontrolle und präzise Anpassungsmöglichkeiten
- Zugang: Die Nutzung ist flexibel über Plattformen wie DreamStudio, Automatic1111 und ComfyUI oder als lokal installierte Lösung möglich.
- Preisgestaltung: Während der Betrieb auf eigener Hardware kostenlos ist, erfolgt die Abrechnung bei Cloud-Anbietern meist auf Basis der generierten Bilder.
- Stärken: Dank der Open-Source-Architektur und einer globalen Community stehen unzählige spezialisierte Modelle zur Verfügung, die bei voller Kontrolle über sämtliche Parameter und ohne Inhaltsbeschränkungen genutzt werden können.
- Schwächen: Die Komplexität setzt technisches Fachwissen voraus und führt zu einer steilen Lernkurve, wobei das Self-Hosting zudem eine leistungsstarke Grafikkarte (GPU) erfordert.
- Ideal für: Technisch versierte Nutzer und Profis, die maximale kreative Kontrolle und Zugriff auf hochspezialisierte Modelle suchen.
Praxiserfahrung: Die investierte Einarbeitungszeit zahlte sich spätestens aus, als hunderte Produktvarianten in einem konsistenten Design erstellt werden mussten – ein Vorhaben, das sich durch die gezielte Feinabstimmung mit individuellen Stable Diffusion-Modellen effizient umsetzen ließ.
Adobe FireflyHervorragend geeignet für den kommerziellen Einsatz
- Zugang: Webbasierte Nutzung mit direkter Integration in die Applikationen der Creative Cloud.
- Preismodell: Vollständig in den bestehenden Creative Cloud-Abonnements enthalten.
- Stärken: Dank des Trainings mit ausschließlich lizenzierten Adobe Stock-Inhalten und gemeinfreien Werken bietet das Tool maximale Urheberrechtssicherheit für die kommerzielle Nutzung. Die nahtlose Einbindung in Photoshop und Illustrator ermöglicht zudem einen hocheffizienten, professionellen Workflow.
- Schwächen: In Bezug auf die reine Bildqualität sowie die stilistische Bandbreite liegt das System teilweise noch hinter Wettbewerbern wie Midjourney oder Stable Diffusion zurück.
- Ideal für: Designer innerhalb des Adobe-Ökosystems sowie für Markenprojekte und kommerzielle Arbeiten, die eine rechtlich abgesicherte Lizenzierung erfordern.
Praxisbericht: Die eindeutige Lizenzierung von Firefly bietet mir bei Kundenprojekten ein Maß an Sicherheit, das andere Tools in dieser Form nicht gewährleisten können.
Spezialisierte Tools, die Sie kennen sollten
Ideogram überzeugt durch die präzise Darstellung von lesbarem Text in Grafiken und meistert damit souverän komplexe Aufgaben wie die Gestaltung von Logos oder Typografie, an denen herkömmliche KI-Modelle oft scheitern.
Leonardo AI Überzeugt besonders bei der Erstellung von Spiele-Assets sowie durch eine hohe Charakterkonsistenz über verschiedene Generierungsdurchläufe hinweg.
Flux Dieses neuartige Modell setzt neue Maßstäbe im Fotorealismus und überzeugt insbesondere durch die präzise Darstellung von Händen – ein Bereich, der für KI-Systeme bislang als eine der größten technischen Hürden galt.
Leitfaden zur Schnellauswahl
Wählen Sie die für Sie optimale Lösung ganz nach Ihren individuellen Anforderungen:
- Überragende ästhetische Qualität: Midjourney setzt den Standard für visuell anspruchsvolle Ergebnisse.
- Benutzerfreundlichkeit und präzise Prompt-Umsetzung: DALL-E-3 überzeugt durch intuitive Bedienung und akkurate Detailtreue.
- Maximale Kontrolle und Individualisierung: Stable Diffusion bietet tiefgreifende Anpassungsmöglichkeiten für professionelle Anwender.
- Kommerzieller Einsatz mit rechtlicher Sicherheit: Adobe Firefly liefert professionelle Resultate unter Einhaltung klarer Lizenzvorgaben.
- Integration von Textelementen: Ideogram spezialisiert sich auf die präzise Darstellung von Schriftzügen innerhalb von Grafiken.
- Herausragender Fotorealismus: Flux und DALL-E-3 sind die führenden Lösungen für detailgetreue und lebensnahe Abbildungen.
Die meisten erfahrenen Anwender setzen auf Abonnements von zwei bis drei verschiedenen Tools, um je nach Projektanforderung flexibel die jeweils am besten geeignete Plattform zu nutzen.
Ein umfassender Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren von Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026 sowie eine detaillierte Analyse ihrer jeweiligen Preisstrategien.
Detaillierter Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026: Ein umfassender Einblick in Funktionen und Preismodelle.Ein umfassender Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren von Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026 sowie eine detaillierte Analyse ihrer jeweiligen Preisstrategien.
Schritt für Schritt zu KI-generierten Bildern: Ein praxisnaher Leitfaden
Da graue Theorie allein nicht ausreicht, zeigen wir Ihnen auf Basis unserer Erfahrung aus tausenden Generierungen, wie Sie in der Praxis wirklich überzeugende KI-Bilder erstellen.
Schritt 1: Die Wahl der passenden Plattform
Um den Einstieg zu erleichtern und direkt erste Erfolgserlebnisse zu schaffen, empfehlen wir, mit der unkompliziertesten Option zu beginnen:
- Einsteiger nutzen idealerweise DALL-E-3 über ChatGPT, da die intuitive Dialogführung einen besonders hürdenfreien Einstieg ermöglicht.
- Für professionelle Kreative ist Midjourney die erste Wahl, da die herausragende Bildqualität die Einarbeitung in die Discord-Umgebung absolut rechtfertigt.
- Preisbewusste Anwender können auf Stable Diffusion zurückgreifen, das über kostenfreie Plattformen wie Hugging Face unkompliziert zugänglich ist.
Schritt 2: Die Grundlagen für effektives Prompting verstehen
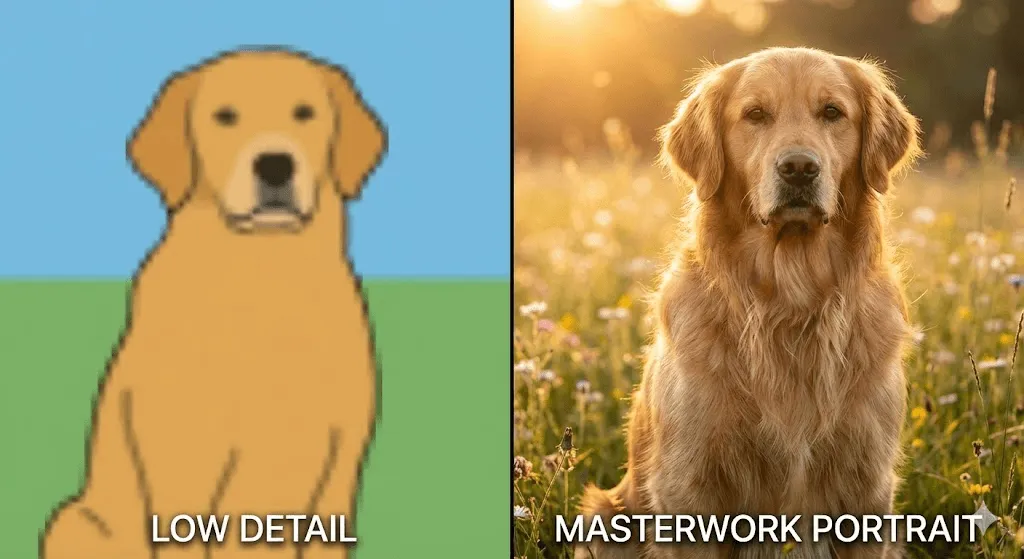

Hier liegt meist die größte anfängliche Hürde, da wirklich effektive Prompts die ideale Balance zwischen präziser Spezifität und prägnanter Kürze erfordern.
Bewährte Strukturen für effektive Prompts:
[Hauptmotiv] + [Aktion/Pose] + [Umgebung/Setting] + [Lichtverhältnisse] + [Stil] + [Technische Details]
Praxisbeispiele:
❌ Unpräzise: „ein Hund“- Oftmals zu vage Formulierungen, die zu unvorhersehbaren Ergebnissen führen
✓ Besser: „Ein Golden Retriever, der in einem Park sitzt“
- Präziser formuliert, dabei jedoch weiterhin leicht verständlich
✓✓ Starker Prompt: „Ein Golden Retriever auf einer Wiese in einem sonnendurchfluteten Park, glücklicher Gesichtsausdruck, geringe Schärfentiefe, Lichtstimmung zur goldenen Stunde, professionelle Tierfotografie, 50-mm-Objektiv“
- Präzise gesteuerte Ergebnisse in professioneller Qualität
Die wichtigsten Grundlagen und Erkenntnisse im Überblick:
- Setzen Sie auf präzise, positive Formulierungen statt auf Verbote, da KI-Modelle direkte Anweisungen deutlich besser verarbeiten als Negationen – wählen Sie also beispielsweise „helle, lebendige Farbpalette“ statt „keine dunklen Farben“.
- Geben Sie konkrete visuelle Stilrichtungen vor, wie etwa „im Stil einer Werbeanzeige aus den 1950er-Jahren“ oder „wie ein Filmstill von Wes Anderson“, um dem Modell eine klare künstlerische Orientierung zu bieten.
- Integrieren Sie fototechnische Fachbegriffe wie „geringe Schärfentiefe“, „Bokeh-Effekt“ oder „Beleuchtung zur Goldenen Stunde“, da diese gezielt die Ästhetik professioneller Fotografie abrufen.
- Beschreiben Sie die gewünschte Emotion oder Grundstimmung: Begriffe wie „behaglich“, „dramatisch“ oder „melancholisch“ beeinflussen die gesamte Bildkomposition sowie die Farbwahl maßgeblich.
- Nutzen Sie verschiedene Seitenverhältnisse und wählen Sie je nach geplantem Verwendungszweck flexibel zwischen Hochformat (9:16), Querformat (16:9) oder quadratischen Layouts (1:1).
Schritt 3: Generierung und Auswertung
Die meisten Plattformen erstellen pro Prompt standardmäßig mehrere Varianten – in der Regel vier verschiedene Optionen –, die Sie anschließend einer kritischen Prüfung unterziehen sollten:
- Entspricht die gesamte Bildkomposition in all ihren Facetten Ihrer gestalterischen Vision?
- Sind das Motiv und seine Details frei von auffälligen Artefakten oder technischen Bildfehlern?
- Vermittelt der gewählte Stil die gewünschte Ästhetik und Tonalität für Ihr Projekt?
- Erfüllt die Grafik in dieser Form die Anforderungen Ihres beabsichtigten Einsatzzwecks?
Perfektion gelingt selten auf Anhieb; meist sind zwei bis drei Durchläufe erforderlich, bevor ein tatsächlich nutzbares Ergebnis erzielt wird.
Schritt 4: Kontinuierliche Iteration und Verfeinerung
Optimieren Sie Ihren Prompt gezielt auf Basis der ersten Ergebnisse, um das gewünschte Bild weiter zu verfeinern:
Sollte die Bildkomposition nicht optimal sein: Passen Sie die Beschreibung der Anordnung im Prompt gezielt an, indem Sie beispielsweise von einer „zentrierten Komposition“ zu einer Platzierung des „Motivs im linken Drittel“ wechseln.
Sollte das Ergebnis stilistisch nicht überzeugen: Verfeinern Sie Ihre Eingabe durch präzisere Stilreferenzen oder passen Sie die verwendeten Keywords gezielt an.
Sollten Details fehlerhaft sein: Verfeinern Sie das Ergebnis, indem Sie die betreffenden Elemente durch präzisere Beschreibungen gezielt ergänzen.
Bei unbeständigen Resultaten lässt sich die Bildqualität durch gezielte Ergänzungen wie „hochdetailliert“, „gestochen scharf“ oder „professionelle Qualität“ effektiv optimieren.
Schritt 5: Nutzen Sie erweiterte Funktionen
Sobald Sie die Grundlagen verinnerlicht haben, erfahren Sie hier mehr über weiterführende Möglichkeiten:
Image-to-Image: Durch das Hochladen eines Referenzbildes lassen sich Komposition, Stil sowie spezifische Bildelemente gezielt steuern und präzise nach Ihren Vorgaben gestalten.
Inpainting: Diese Funktion ermöglicht die gezielte Neugenerierung einzelner Bildabschnitte unter Beibehaltung des restlichen Inhalts, was besonders für präzise Detailkorrekturen ideal ist.
Outpainting: Erweitern Sie bestehende Aufnahmen nahtlos über ihre ursprünglichen Bildränder hinaus.
Upscaling: Steigern Sie die Bildauflösung bei gleichbleibender Qualität, wobei diese Funktion entweder bereits nativ in die Plattform integriert ist oder den Einsatz spezialisierter externer Tools erfordert.
Schritt 6: Die Nachbearbeitung
Selbst erstklassige KI-Ergebnisse profitieren häufig von einem abschließenden menschlichen Feinschliff:
- Optimierung der Bildkomposition durch gezielten Zuschnitt
- Professionelle Farbkorrektur sowie präzises Color Grading
- Retusche kleinerer Bildfehler und störender Artefakte
- Einbindung von Textelementen oder grafischen Ergänzungen
- Nahtlose Kombination und Zusammenführung mehrerer Bildergebnisse
Hierfür lassen sich professionelle Werkzeuge wie Photoshop oder GIMP einsetzen, während für grundlegende Korrekturen bereits einfache Bildbearbeitungs-Apps völlig ausreichen.
Ein umfassender Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren von Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026 sowie eine detaillierte Analyse ihrer jeweiligen Preisstrategien.
Detaillierter Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026: Ein umfassender Einblick in Funktionen und Preismodelle.Ein umfassender Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren von Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026 sowie eine detaillierte Analyse ihrer jeweiligen Preisstrategien.
So erkennen Sie KI-generierte Bilder

Da sich diese Technologien stetig weiterentwickeln, fällt die Abgrenzung zwischen KI-generierten Bildern, echten Fotografien und menschlicher Kunst immer schwerer, wenngleich derzeit noch charakteristische Merkmale auf den Einsatz künstlicher Intelligenz hindeuten.
Typische visuelle Anomalien und Fehlerquellen
Anatomische Unstimmigkeiten:
Trotz der signifikanten technologischen Fortschritte stößt die KI in bestimmten Bereichen gelegentlich noch an ihre Grenzen:
- Hände, die häufig durch zusätzliche oder fehlende Finger, anatomisch unnatürliche Haltungen sowie miteinander verwachsene Gliedmaßen auffallen.
- Zahnstrukturen, die oft in zu großer Zahl, mit unregelmäßigen Mustern oder in anatomisch unkorrekten Anordnungen generiert werden.
- Augenpartien, bei denen asymmetrische Pupillen, eine uneinheitliche Blickrichtung oder unnatürliche Lichtreflexionen auftreten.
- Komplexe Körpermechanik, die sich in falsch gebogenen Gelenken oder unklaren anatomischen Verbindungen zwischen den Gliedmaßen äußert.
Während moderne Modelle wie DALL-E-3 und Flux die Problematik bei der Darstellung von Händen weitestgehend gelöst haben, kann es vereinzelt dennoch zu Fehlern kommen.
Herausforderungen bei Textdarstellung und Typografie:
Die präzise Darstellung von Textelementen stellt für die meisten Modelle nach wie vor eine erhebliche Herausforderung dar:
- Unleserliche Zeichenfolgen, die lediglich die Form von Buchstaben imitieren
- Inkonsistente Schriftarten und Stilbrüche innerhalb einzelner Schriftzüge
- Spiegelverkehrte Darstellungen oder fehlerhaft rückwärts geschriebene Texte
- Unvollständig generierte oder ineinander verschwimmende Buchstabenformen
Ideogram bildet hierbei eine wesentliche Ausnahme, da es sich auf die präzise Textdarstellung spezialisiert hat und diese weitaus effektiver umsetzt als konkurrierende Lösungen.
Physikalische Unmöglichkeiten:
- Inkonsistente Lichtführung mit widersprüchlichen Einfallswinkeln
- Schattenverläufe, die nicht mit den im Bild vorhandenen Lichtquellen harmonieren
- Spiegelungen, die fehlerhafte oder unlogische Bildinhalte wiedergeben
- Perspektivische Fehler, wie etwa Gebäude in physikalisch unmöglichen Winkeln
- Objekte, die den grundlegenden Gesetzen der Physik trotzen
Herausforderungen bei Texturen und Details:
- Unnatürlich glatte Hautoberflächen mit einer künstlichen, plastikartigen Textur
- Repetitive Musterabfolgen an Stellen, die eigentlich natürliche Variationen erfordern
- Eine auffällig makellose, oft unnatürlich wirkende Symmetrie
- Hintergrundelemente, die diffus wirken und inkohärent ineinander verschwimmen
- Deformierte oder ineinander verschmelzende Detailstrukturen an den Bildrändern
Stilistische Erkennungsmerkmale
Die charakteristische KI-Ästhetik:
Wer bereits tausende von KI-generierten Bildern gesichtet hat, entwickelt mit der Zeit ein geschultes Auge für deren ganz spezifische Ästhetik und visuelle Charakteristik:
- Stark gesättigte und übernatürlich leuchtende Farben, wie sie insbesondere für Ergebnisse aus Midjourney charakteristisch sind
- Eine exzessive Nutzung von Bokeh-Effekten sowie eine extreme Tiefenunschärfe zur künstlichen Akzentuierung
- Eine unnatürlich dramatische, cineastische Lichtführung, die selbst alltäglichen Szenen eine übersteigerte Atmosphäre verleiht
- Übermäßig perfekt ausbalancierte Bildkompositionen, die in ihrer Makellosigkeit oft unnatürlich wirken
- Eine charakteristische, synthetische Oberflächenglätte, die feinen Details ihren natürlichen Charakter nimmt
Makellose Perfektion in Bestform:
Während KI-generierte Bilder meist zu einer idealisierten, kommerziellen Ästhetik neigen, zeichnet sich echte Fotografie gerade durch jene authentischen Unvollkommenheiten wie Staubpartikel, leichte Unschärfen oder unvorteilhafte Perspektiven aus, die von der künstlichen Intelligenz üblicherweise vermieden werden.
Kontextuelle Anhaltspunkte
Oftmals lässt erst der Kontext auf eine KI-Generierung schließen, noch bevor das eigentliche Bild eindeutige Merkmale preisgibt:
- Erscheint das Szenario für eine reale Fotografie zu außergewöhnlich oder gar unrealistisch?
- Wäre die Umsetzung des Motivs in der Realität nur unter extrem hohem Kosten- oder Zeitaufwand möglich?
- Gibt der Urheber an, innerhalb kürzester Zeit eine Vielzahl komplexer und aufwendig gestalteter Szenen erstellt zu haben?
- Weisen verschiedene Werke trotz unterschiedlicher Themen eine auffallend konsistente, nahezu identische Stilistik auf?
KI-Erkennungstools
Mittlerweile bieten diverse Dienste spezialisierte Lösungen zur Identifizierung von KI-generierten Bildern an:
- Der Hive AI Detector liefert präzise Wahrscheinlichkeitswerte zur Identifizierung generierter Inhalte.
- Illuminarty analysiert Bilddaten systematisch auf charakteristische Signaturen künstlicher Intelligenz.
- Optic ermöglicht die gezielte Bestimmung der für die Erstellung genutzten KI-Modelle.
Dennoch sind diese Tools keineswegs unfehlbar, da sich die Identifizierung von Inhalten angesichts der rasanten KI-Entwicklung zu einem technologischen Wettrüsten entwickelt hat. Wie eine Studie der University of California aus dem Jahr 2024 belegt, können selbst geschulte Experten KI-generierte Bilder lediglich in 60 bis 70 % der Fälle zuverlässig identifizieren.
Ein Blick auf das große Ganze
Da eine lückenlose Erkennung künftig nahezu unmöglich sein wird, stellen sich grundlegende Fragen zur Bildauthentizität, die uns direkt zu den damit verbundenen Herausforderungen führen.
Ein umfassender Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren von Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026 sowie eine detaillierte Analyse ihrer jeweiligen Preisstrategien.
Detaillierter Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026: Ein umfassender Einblick in Funktionen und Preismodelle.Ein umfassender Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren von Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026 sowie eine detaillierte Analyse ihrer jeweiligen Preisstrategien.
Branchenübergreifende Anwendungsmöglichkeiten in der Praxis
Die KI-Bildgenerierung hat sich längst über rein experimentelle Anwendungen hinaus zu einem unverzichtbaren Werkzeug im professionellen Geschäftsumfeld entwickelt, wobei sich in der täglichen Praxis bereits heute zeigt, welche Ansätze tatsächlich zum Erfolg führen.
Marketing und Werbung
Anwendungsbeispiel: Ein kleines E-Commerce-Unternehmen nutzt die Technologie, um Möbel in verschiedensten Wohnumgebungen und Stilrichtungen zu inszenieren – ein Projekt, das mit herkömmlicher Fotografie Kosten von über 10.000 $ verursachen würde.
Kostenvergleich
- Herkömmliche Fotoshootings verursachen pro Termin Kosten zwischen 2.000 und 5.000 $, was bei mehreren Einsätzen ein Budget von über 20.000 $ beansprucht.
- Mit einem KI-gestützten Modell lassen sich diese Ausgaben bei einem monatlichen Abonnement von 30 $ auf insgesamt weniger als 500 $ reduzieren.
Praxisbeispiel: Der Möbelhändler Wayfair konnte im Jahr 2023 durch den Einsatz KI-generierter Raumszenen seine Content-Produktion um 40 % beschleunigen und dabei gleichzeitig signifikante Kosteneinsparungen realisieren.
Erstellung von Inhalten
Anwendungsbereich: Blogger, YouTuber und Podcaster sind kontinuierlich auf individuelles Bildmaterial angewiesen, wobei die KI-Generierung eine ideale Lösung bietet, um ohne den komplexen Lizenzierungsaufwand herkömmlicher Stockfotos einzigartige und markengerechte Visuals zu erstellen.
Sämtliche Header-Grafiken für meinen Blog erstelle ich mittlerweile mit Midjourney, wodurch sich der Zeitaufwand pro Artikel von den üblichen 30 bis 45 Minuten für die aufwendige Stockfoto-Recherche auf lediglich 10 bis 15 Minuten reduziert.
E-Commerce und Produktvisualisierung
Anwendungsbeispiel: Die Visualisierung von Produkten in noch nicht existierenden Umgebungen ermöglicht es etwa Modemarken, hunderte Outfit-Kombinationen an verschiedensten Modellen digital zu präsentieren, noch bevor die eigentliche Produktion physischer Muster beginnt.
Ihr Vorteil: Testen Sie die Marktresonanz bereits vor der eigentlichen Fertigung, um potenzielle Lagerrisiken effektiv zu minimieren.
Spieleentwicklung und Entertainment
Anwendungsbereich: Indie-Spieleentwickler nutzen die Technologie bereits in der Vorproduktionsphase, um effizient Concept Art, Umgebungsreferenzen sowie detaillierte Charakterdesigns zu entwerfen.
Praxisbeispiel: Bei Titeln wie „Citizen Sleeper“ wurden KI-generierte Grafiken gezielt für Hintergründe und Konzeptelemente eingesetzt, wodurch selbst kleine Teams eine visuelle Komplexität realisieren konnten, die üblicherweise weitaus größeren Studios vorbehalten bleibt.
Architektur und Innenarchitektur
Anwendungsbereich: Visualisieren Sie verschiedene Designansätze für Kundenpräsentationen in kürzester Zeit und erstellen Sie vielseitige Raumlayouts, Fassadenoptionen oder Landschaftskonzepte innerhalb weniger Stunden statt in mehreren Tagen.
Ein mir bekannter Architekt nutzt Stable Diffusion, um zunächst 20 bis 30 verschiedene Konzeptentwürfe zu erstellen, wovon er die zwei bis drei Favoriten seiner Kunden manuell weiter ausarbeitet – ein Vorgehen, das die frühe Kreativphase massiv beschleunigt.
Wissen & Grundlagen
Anwendungsfall: Lehrkräfte erstellen maßgeschneiderte Illustrationen für ihre Unterrichtsplanung, wodurch visuelle Inhalte wie historische Szenen, wissenschaftliche Diagramme oder literarische Interpretationen punktgenau auf den jeweiligen Lehrplan zugeschnitten werden können.
Beispiel: Eine Geschichtslehrkraft erstellt visuelle Darstellungen von Ereignissen, ohne dabei auf potenziell ungenaue oder voreingenommene historische Gemälde angewiesen zu sein.
Die Grenzen der KI-Bildgenerierung
Dabei liefern längst nicht alle Anwendungen gleichermaßen hochwertige Ergebnisse:
❌ Technische Dokumentation Da die KI die hier zwingend erforderliche Präzision nicht durchgängig gewährleisten kann ❌ Medizin und Recht In diesen sensiblen Bereichen sind die Risiken automatisierter Inhalte schlichtweg zu hoch ❌ Kunstmarkt Hier behalten handgefertigte Originale gegenüber KI-Werken ihren einzigartigen, menschlichen Wert ❌ Fotojournalismus Da Authentizität hier die Grundlage bildet, wäre der Einsatz generierter Bilder ethisch nicht vertretbar
Ein umfassender Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren von Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026 sowie eine detaillierte Analyse ihrer jeweiligen Preisstrategien.
Detaillierter Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026: Ein umfassender Einblick in Funktionen und Preismodelle.Ein umfassender Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren von Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026 sowie eine detaillierte Analyse ihrer jeweiligen Preisstrategien.
Grenzen, Herausforderungen und Kontroversen

Ein fundiertes Verständnis der KI-Bildgenerierung setzt eine ehrliche Auseinandersetzung mit ihren aktuellen Herausforderungen und noch ungelösten Fragestellungen voraus.
Urheberrecht und rechtliche Unsicherheiten
Die zentrale Problematik: Ein Großteil der KI-Modelle basiert auf dem Training mit Milliarden aus dem Internet extrahierten Bildern, wobei Kunstwerke, Fotografien und Illustrationen häufig ohne die ausdrückliche Zustimmung oder eine entsprechende Vergütung der Urheber verwendet werden.
Die Perspektive der Kunstschaffenden: Viele Kreative sehen in der Nutzung ihrer Werke zum Training konkurrierender KI-Modelle eine unrechtmäßige Aneignung, was zu laufenden Sammelklagen gegen Anbieter wie OpenAI, Stability AI und Midjourney geführt hat.
Die Sicht der Unternehmen: Das Training wird als rechtmäßige Nutzung („Fair Use“) eingestuft, da die KI – ähnlich wie der Mensch – lediglich durch die Analyse bestehender Werke lernt, ohne dabei Bildmaterial direkt zu speichern oder zu reproduzieren.
Aktuelle Rechtslage: Die rechtliche Situation ist derzeit noch ungeklärt, da Gerichte voraussichtlich Jahre benötigen werden, um wegweisende Präzedenzfälle zu schaffen, die den künftigen Einsatzrahmen dieser Tools maßgeblich definieren werden.
Eigentumsrechte am Output: Zur Frage, wem ein KI-generiertes Bild gehört, geben die aktuellen Richtlinien des U.S. Copyright Office Aufschluss: Während rein KI-basierten Werken mangels ausreichender menschlicher Schöpfungshöhe der Urheberrechtsschutz meist verwehrt bleibt, können Arbeiten mit maßgeblicher menschlicher Beteiligung durchaus schutzfähig sein.
Praxishinweis: Bei der kommerziellen Nutzung von KI-Bildern sollten Sie die derzeitige rechtliche Unsicherheit berücksichtigen; so bietet etwa Adobe Firefly durch das Training mit ausschließlich lizenzierten Inhalten zwar eine höhere Rechtssicherheit, schränkt dadurch jedoch unter Umständen die kreative Vielfalt der Ergebnisse ein.
Der Einfluss auf die Arbeit von Kreativschaffenden
Die unbequeme Wahrheit: Die KI-basierte Bildgenerierung verdrängt unweigerlich bestimmte, bislang manuell ausgeführte Arbeitsschritte, was insbesondere für folgende Bereiche gilt:
- Stockfotografie für den allgemeinen kommerziellen Bedarf
- Einfache Illustrationsarbeiten
- Spezifische Bereiche des Grafikdesigns
- Concept Art zur ersten visuellen Ideenfindung
Eine Umfrage der Concept Art Association aus dem Jahr 2023 belegt, dass 67 % der professionellen Illustratoren einen Rückgang ihrer Aufträge verzeichnen – eine Entwicklung, die von vielen direkt mit dem Aufkommen von KI-Tools in Verbindung gebracht wird.
Gegenperspektive: Durch neue Spezialisierungen wie Prompt Engineering oder AI Art Direction etablieren sich innovative, hybride Workflows, bei denen KI-gestützte Prozesse durch menschliche Veredelung ergänzt werden. Historische Entwicklungen lassen darauf schließen, dass Technologie das kreative Schaffen eher transformiert als verdrängt, wenngleich dies für jene, die derzeit von diesen Umbrüchen betroffen sind, nur wenig Trost bietet.
Meine Beobachtung: Die erfolgreichsten Kreativprofis betrachten KI nicht als Konkurrenz, sondern integrieren sie als wertvolles Werkzeug in ihren Workflow, um Arbeitsschritte effizient zu beschleunigen und die Ergebnisse anschließend mit ihrer einzigartigen menschlichen Intuition zu vollenden.
Ethische Bedenken
Deepfakes und Desinformation: Dieselbe Technologie, die zur Erzeugung von KI-Kunst dient, kann ebenso zur Erstellung täuschend echter Aufnahmen von fiktiven Ereignissen sowie zur Manipulation von Beweismaterial oder zur Darstellung von Personen in kompromittierenden Situationen missbraucht werden.
Zu den bekanntesten aktuellen Beispielen gehören KI-generierte Bilder des Papstes in modischer Designerkleidung, die als virale Fälschungen weltweit Schlagzeilen machten, sowie manipulierte Darstellungen von Politikern in fiktiven Szenarien.
Voreingenommenheit und Repräsentativität: Da KI-Modelle zwangsläufig die in ihren Trainingsdaten enthaltenen Vorurteile übernehmen, sahen sich frühe Bildgeneratoren massiver Kritik in folgenden Bereichen gegenüber:
- Die Neigung zu stereotypen Darstellungen, die oft auf herkömmlichen Mustern basieren
- Eine unzureichende Repräsentation verschiedener demografischer Bevölkerungsgruppen
- Die daraus resultierende Verstärkung und Verstetigung schädlicher gesellschaftlicher Vorurteile
- Eine eingeschränkte Diversität bei der Visualisierung von Attributen wie Professionalität oder Attraktivität
Trotz der bereits erzielten Fortschritte stellt die Überwindung von Verzerrungen und Vorurteilen weiterhin eine zentrale Herausforderung dar.
Ökologische Auswirkungen: Da das Training komplexer KI-Modelle immense Rechenkapazitäten beansprucht, emittiert ein einzelner Trainingsvorgang laut einer Studie der University of Massachusetts Amherst aus dem Jahr 2019 so viel CO2 wie fünf Pkw über ihre gesamte Lebensdauer. Auch wenn die eigentliche Bildgenerierung deutlich weniger Ressourcen benötigt, ist die Berücksichtigung der kumulativen Umweltbelastung dieser Technologien unerlässlich.
Technische Grenzen und Limitierungen
Trotz ihrer beeindruckenden technologischen Möglichkeiten stößt die moderne KI-Bildgenerierung in der Praxis noch immer auf spezifische Herausforderungen:
Konsistenz: Die durchgängige Darstellung derselben Charaktere oder Objekte über mehrere Bilder hinweg bleibt eine technologische Herausforderung. Trotz deutlicher Fortschritte – wie etwa den neuen Funktionen für Charakter-Referenzen in Midjourney – stoßen die meisten Tools bei der Erzielung vollkommener Konsistenz derzeit noch an ihre Grenzen.
Präzise Kontrolle: Die exakte Umsetzung Ihrer Vision hinsichtlich Komposition, Farbwahl und Details erfordert oft zahlreiche Iterationen, da die „Generierungslotterie“ selbst bei ähnlichen Prompts zu qualitativ unterschiedlichen Ergebnissen führen kann.
Spezifische technische Anforderungen: Ob präzise Produktdarstellungen, architektonische Genauigkeit oder technische Diagramme – häufig entsprechen die Ergebnisse nicht den hohen Standards, die professionelle Anwender voraussetzen.
Kontextuelles Verständnis: Da die KI Bilder auf Basis visueller Muster statt eines echten begrifflichen Verständnisses generiert, können Resultate zwar optisch überzeugend wirken, sich jedoch als inhaltlich unlogische Kombinationen erweisen.
Skalierungskosten: Während die Erstellung einzelner Bilder kostengünstig ist, kann die Generierung tausender Grafiken für Großprojekte bei kommerziellen Plattformen schnell zu einem erheblichen Kostenfaktor werden.
Ein umfassender Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren von Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026 sowie eine detaillierte Analyse ihrer jeweiligen Preisstrategien.
Detaillierter Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026: Ein umfassender Einblick in Funktionen und Preismodelle.Ein umfassender Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren von Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026 sowie eine detaillierte Analyse ihrer jeweiligen Preisstrategien.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Darf ich KI-generierte Bilder für kommerzielle Zwecke nutzen?
Die kommerzielle Nutzung richtet sich nach den jeweiligen Plattform-AGB sowie Ihrem Abonnement-Status, wobei Anbieter wie Midjourney, DALL-E und Adobe Firefly die gewerbliche Verwendung in ihren kostenpflichtigen Tarifen grundsätzlich erlauben. Da die rechtliche Situation rund um das Urheberrecht jedoch weiterhin komplex ist und bestimmte Anwendungsbereiche, wie der Verkauf reiner KI-Kunstdrucke, eine Grauzone darstellen, sollten Sie die spezifischen Bedingungen stets sorgfältig prüfen und bei geschäftskritischen Projekten eine rechtliche Beratung hinzuziehen.
Wird die Künstliche Intelligenz menschliche Künstler und Fotografen künftig ersetzen?
Zwar ist eine vollständige Verdrängung dieser Berufsbilder unwahrscheinlich, doch wird die KI-Technologie sie grundlegend transformieren. Während die Künstliche Intelligenz ihre Stärken vor allem bei der effizienten Erstellung von Stockmaterial, der schnellen Konzeptentwicklung oder der Produktion großer Inhaltsmengen ausspielt, bleiben menschliche Fähigkeiten in Bereichen wie konzeptionellem Denken, emotionalen Nuancen und der Pflege von Kundenbeziehungen unverzichtbar. Vielmehr wird sich die KI als fester Bestandteil moderner Workflows etablieren – vergleichbar mit der Einführung von Photoshop, das die Fotografie revolutionierte, ohne sie jemals zu ersetzen.
Woran lässt sich erkennen, ob ein Bild mithilfe von Künstlicher Intelligenz erstellt wurde?
Zur Identifizierung von KI-Inhalten empfiehlt sich ein Blick auf visuelle Anomalien wie fehlerhafte Handdarstellungen, unlogische Texte oder Lichtinkonsistenzen, kombiniert mit typischen Stilmerkmalen wie extremer Farbsättigung und dem markanten „KI-Look“. Da Detektionslösungen wie der Hive AI Detector keine absolute Sicherheit garantieren, wird die Unterscheidung mit zunehmender Modellreife selbst für Fachleute immer anspruchsvoller, da die Grenzen zwischen Realität und künstlicher Generierung zunehmend verschwimmen.
Speichern oder vervielfältigen KI-Bildgeneratoren die Bilddaten, die als Grundlage für ihr Training dienten?
Nein, denn im Trainingsprozess wird keine Bilddatenbank angelegt, sondern ein mathematisches Modell erstellt, das lediglich Muster innerhalb von Bildern repräsentiert. Anstatt die Trainingsdaten selbst zu speichern, erlernt das Modell abstrakte Konzepte – wie etwa das Aussehen einer Katze oder die Charakteristika der Aquarellmalerei –, wobei die gelegentliche Ähnlichkeit der generierten Ergebnisse mit berühmten Kunstwerken ein zentraler Aspekt der aktuellen Urheberrechtsdebatte ist.
Welcher KI-Bildgenerator liefert die besten Ergebnisse?
Den einen, universell besten Bildgenerator gibt es nicht – die ideale Wahl hängt vielmehr ganz von Ihren individuellen Anforderungen ab:
- Höchste ästhetische Qualität und Bildpräzision: Midjourney
- Überlegene Genauigkeit bei der Prompt-Umsetzung: DALL-E 3
- Maximale Kontrolle und gestalterische Flexibilität: Stable Diffusion
- Optimiert für professionelle kommerzielle Anwendungen: Adobe Firefly
- Führend bei der Integration von Textelementen in Grafiken: Ideogram
- Bestes Preis-Leistungs-Verhältnis: Stable Diffusion (kostenlos) oder Midjourney Basic (10 $/Monat)
Im professionellen Umfeld kommen meist verschiedene Tools zum Einsatz, um den jeweils spezifischen Anforderungen optimal gerecht zu werden.
Wie steht es um die ethische Vertretbarkeit beim Einsatz von KI-Bildgeneratoren?
Die Debatte über den Einsatz von KI bleibt vielschichtig: Während Befürworter die Demokratisierung der Kreativität sowie neue Ausdrucksformen für kleine Unternehmen und Content Creator hervorheben, warnen Kritiker vor der unbefugten Nutzung künstlerischer Werke, der Verdrängung menschlicher Fachkräfte und der Verbreitung von Fehlinformationen. Angesichts dieser Spannungsfelder fordern viele Anwender neben der aktiven Nutzung auch klare Regulierungen, faire Vergütungssysteme sowie ethische Trainingsstandards, sodass eine fundierte Auseinandersetzung mit diesen Aspekten für eine verantwortungsbewusste eigene Haltung unerlässlich ist.
Kann künstliche Intelligenz fotorealistische Bilder von realen Personen generieren?
Rein technisch ist dies zwar möglich, jedoch untersagen die meisten Plattformen die Erstellung von Bildern identifizierbarer Personen ohne deren ausdrückliche Genehmigung. Da die Generierung von Fake-Bildern realer Personen – insbesondere von Persönlichkeiten des öffentlichen Lebens – erhebliche ethische sowie rechtliche Bedenken aufwirft, unterbinden Dienste wie DALL E derartige Versuche aktiv. Setzen Sie KI-Tools daher keinesfalls ein, um irreführende oder diffamierende Darstellungen echter Personen zu erzeugen.
Welche Kosten entstehen bei der KI-Bildgenerierung?
- Kostenlose Optionen: Neben selbst gehosteten Lösungen wie Stable Diffusion bieten die meisten Plattformen zeitlich oder funktional begrenzte Gratis-Modelle an.
- Preiswerte Einsteiger-Tarife: Ab etwa 10 USD pro Monat lassen sich Dienste wie Midjourney Basic oder verschiedene Stable-Diffusion-Plattformen nutzen.
- Standard-Nutzung: Für monatlich 20 bis 30 USD erhalten Anwender Zugriff auf DALL-E via ChatGPT Plus oder den Midjourney-Standard-Tarif.
- Professionelle Lösungen: Ab 50 bis über 100 USD pro Monat profitieren Profis von höheren Nutzungslimits, erweiterten Funktionen und umfassenden kommerziellen Lizenzrechten.
Die Kosten pro Bildgenerierung variieren erheblich und reichen von nahezu kostenlosen, selbst gehosteten Lösungen wie Stable Diffusion bis hin zu kommerziellen Plattformen, bei denen pro Erstellung meist zwischen 0,10 $ und 0,50 $ anfallen.
Ein umfassender Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren von Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026 sowie eine detaillierte Analyse ihrer jeweiligen Preisstrategien.
Detaillierter Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026: Ein umfassender Einblick in Funktionen und Preismodelle.Ein umfassender Vergleich der KI-Bildgeneratoren von Ideogram und Midjourney für das Jahr 2026 sowie eine detaillierte Analyse ihrer jeweiligen Preisstrategien.
Fazit
Die KI-Bildgenerierung markiert einen wegweisenden technologischen Wandel in der Erstellung visueller Inhalte und bietet durch ihre beeindruckende Leistungsfähigkeit, Schnelligkeit sowie Wirtschaftlichkeit einen echten Mehrwert für verschiedenste Einsatzbereiche.
Gleichzeitig wirft diese Entwicklung komplexe, noch ungeklärte Fragen zu Urheberrechten, dem Wert kreativer Arbeit sowie der Authentizität von Bildmaterial auf, mit denen sich unsere Gesellschaft intensiv auseinandersetzen muss. Während die Technologie stetig reift, schärft sich parallel dazu unser Verständnis für ihre verantwortungsvolle Anwendung sowie die Notwendigkeit klar definierter Grenzen.
In der heutigen digitalen Landschaft ist fundiertes Wissen über KI-Bildgenerierung für Fachkräfte in Content-Erstellung, Marketing und Kreativwirtschaft längst unverzichtbar geworden. Die bewusste Entscheidung für den Einsatz dieser Tools sowie der strategische Umgang mit ihren Potenzialen werden dabei maßgeblich die nächste Ära der visuellen Content-Produktion definieren.
Der effektivste Weg zum Erfolg liegt darin, KI nicht als Ersatz, sondern als leistungsstarken Assistenten zu betrachten, der Workflows beschleunigt und die Exploration neuer Ideen bei hohem Volumen unterstützt. Durch die anschließende Veredelung mittels menschlicher Kreativität und Urteilskraft entstehen so Resultate, welche die spezifischen Stärken beider Seiten optimal miteinander kombinieren.