What Is AI Art? The Definitive Guide to AI Generated Art in 2026
Last Updated: 2026-01-22 18:07:43

In the past three years, AI art has transformed from a niche technological experiment into a cultural phenomenon that's reshaping how we create, consume, and think about visual content. From viral social media images to award winning gallery pieces, AI-generated artwork is everywhere and it's only getting more sophisticated.
But what exactly is AI art? How does it work? And why has it sparked such intense debate among artists, technologists, and legal experts alike?
This comprehensive guide answers every question you have about artificial intelligence art from the fundamental technology behind text to image generators to the ethical controversies shaping its future. Whether you're a curious beginner, a creative professional exploring new tools, or someone trying to understand the implications of this technology, you'll find everything you need here.
Key Takeaway: AI art refers to visual artwork created using artificial intelligence algorithms typically by converting text descriptions (prompts) into images. While the technology has democratized image creation, it raises significant questions about creativity, copyright, and the future of human artists.
What Is AI Art? A Clear Definition
AI art (also called AI generated art or generative AI art) is visual artwork created with the assistance of artificial intelligence systems. These systems use machine learning algorithms trained on millions of existing images to generate new, original visuals based on user inputs typically text descriptions called "prompts."
Unlike traditional digital art, which requires manual creation by a human artist using tools like Photoshop or Illustrator, AI art emerges from a collaboration between human intention and machine computation. The user provides creative direction through prompts, while the AI handles the technical execution of rendering the image.
AI Art vs. Digital Art vs. Traditional Art
Aspect | AI Art | Digital Art | Traditional Art |
Creation Method | Text prompts + AI algorithms | Manual creation with software | Physical media (paint, pencil) |
Skill Required | Prompt engineering | Software proficiency + artistry | Years of practice + technique |
Time to Create | Seconds to minutes | Hours to days | Days to months |
Reproducibility | Infinitely reproducible | Infinitely reproducible | One of a kind original |
A Brief History of AI Art: From AARON to DALL E
While AI art exploded into mainstream consciousness in 2022, the concept has roots stretching back over five decades. Understanding this history helps contextualize where the technology is today and where it's headed.
The Pioneers (1960s~2010s)
1973: AARON Computer scientist Harold Cohen developed AARON, widely considered the first AI art program. Unlike modern systems, AARON followed explicit rules Cohen programmed to create abstract drawings and paintings. The system continued evolving until Cohen's death in 2016.
2014: Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) Researcher Ian Goodfellow introduced GANs, a breakthrough architecture that would revolutionize AI image generation. GANs use two competing neural networks a generator and a discriminator to create increasingly realistic outputs.
2015: DeepDream Google's Alexander Mordvintsev created DeepDream, which produced distinctive psychedelic images by amplifying patterns a neural network detected in existing photos. These trippy, eye filled images became the first AI art to achieve viral internet fame.
The Modern Era (2021~Present)
January 2021: DALL E OpenAI unveiled DALL E, the first large scale text to image model capable of generating coherent images from natural language descriptions. Named as a portmanteau of Salvador Dalí and Pixar's WALL E, it demonstrated unprecedented creative flexibility.
July 2022: Midjourney Independent research lab Midjourney launched its eponymous image generator, quickly gaining a reputation for distinctive, artistic outputs with a painterly quality that set it apart from competitors.
August 2022: Stable Diffusion Stability AI released Stable Diffusion as an open source model, democratizing access to AI image generation. Unlike proprietary alternatives, anyone could run it locally, modify its code, or train custom versions.
2023~2025: Rapid Evolution The field exploded with improvements in image quality, consistency, and control. DALL E 3 integrated directly with ChatGPT, Midjourney v6 and v7 achieved photorealistic quality, and new models like Flux, Reve Image, and Ideogram pushed boundaries in specific areas like text rendering and prompt adherence.
How Do AI Art Generators Work? The Technology Explained
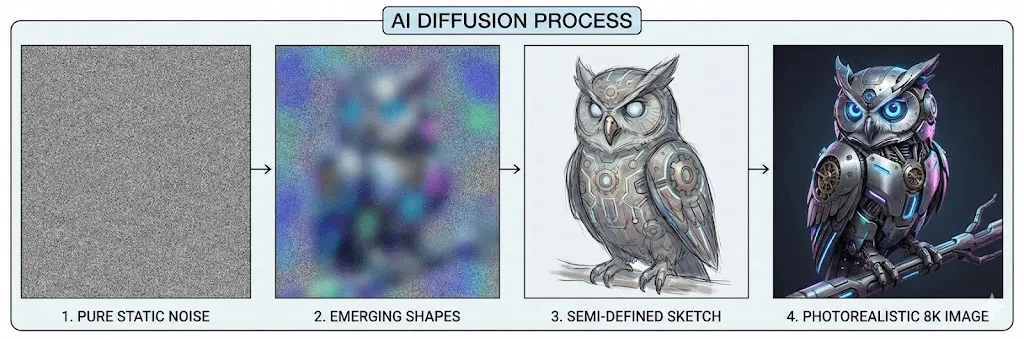
Understanding how AI creates images helps demystify the technology and reveals why these systems are both remarkably capable and inherently limited. Modern text to image AI relies on three core components working together.
Component 1: The Training Dataset
Every AI art generator begins with massive datasets of images paired with text descriptions. These datasets containing hundreds of millions to billions of image text pairs are scraped from the internet, including art websites, stock photo libraries, and social media platforms.
During training, the AI learns patterns and associations: what "sunset" looks like, how "impressionist" style differs from "photorealistic," and what visual elements correspond to countless concepts. The quality and diversity of training data directly impacts what the AI can generate.
Component 2: The Neural Network Architecture
Most modern AI art generators use one of two primary architectures:
Diffusion Models (used by Stable Diffusion, DALL E 2/3, Midjourney): These work by learning to reverse a gradual noising process. During training, the model learns how to reconstruct images from pure noise, step by step. During generation, it starts with random noise and iteratively refines it into a coherent image matching the text prompt.
Transformer Models (used by DALL E 1, Parti): These treat image generation like language translation, predicting image tokens sequentially based on text input. While less common now, transformers remain important for understanding text prompts.
Component 3: The Text Encoder
Before the AI can generate an image, it must understand your text promptly. Text encoders often based on models like CLIP (Contrastive Language Image Pre training) convert your words into a numerical representation the image generator can work with. These encoders understand not just individual words but relationships between concepts, enabling prompts like "a cat wearing a top hat in the style of Van Gogh."
The Generation Process Step by Step
- Prompt Encoding: Your text prompt is converted into a numerical "embedding" that captures its semantic meaning.
- Noise Initialization: The system starts with random noise (for diffusion models) or an empty canvas.
- Iterative Refinement: Over 20~50 steps, the model gradually shapes the noise into an image, guided by the prompt embedding.
- Upscaling (Optional): Many systems add a final step to enhance resolution and detail.
Important Clarification: AI image generators do not store or retrieve existing images. They learn statistical patterns from training data and use those learned patterns to generate entirely new images. Think of it like how a human artist learns from studying many paintings without copying any single one.

Best AI Art Generators in 2026: Complete Comparison
The AI art generator landscape has matured significantly, with different tools excelling in different areas. Here's a comprehensive breakdown of the leading options.
Midjourney
Best for: Artistic, stylized images with exceptional aesthetic quality
Midjourney has earned a reputation as the "artist's choice" among AI generators. Its outputs tend toward the painterly and cinematic, with rich colors, dramatic lighting, and a distinctive "Midjourney look" that's immediately recognizable. Version 7 (released April 2025) significantly improved text rendering and character consistency.
- Exceptional aesthetic quality out of the box
- Strong community and prompt sharing ecosystem
- Now available via web interface (previously Discord only)
- Pricing: From $10/month for ~200 images
ChatGPT / GPT 4o Image Generation
Best for: Conversational image creation and iterative refinement
OpenAI's integration of image generation directly into ChatGPT has made AI art more accessible than ever. The conversational interface lets users refine images through natural dialogue ("make the sky more dramatic" or "add a person in the foreground"), lowering the barrier to entry significantly.
- Intuitive conversational workflow
- Excellent prompt interpretation
- Strong at photorealistic images
- Pricing: Included with ChatGPT Plus ($20/month)
Stable Diffusion
Best for: Maximum control, customization, and local/private use
As the leading open source option, Stable Diffusion offers unmatched flexibility. Users can run it locally (no internet required), train custom models on specific styles or subjects, and avoid content restrictions present in commercial tools. The tradeoff is a steeper learning curve.
- Completely free and open source
- Extensive customization through fine tuning and LoRAs
- Large ecosystem of community models and extensions
- Pricing: Free (requires capable GPU for local use)
Adobe Firefly
Best for: Commercial use and Creative Cloud integration
Adobe's entry into AI art stands out for one crucial reason: it's trained exclusively on licensed content (Adobe Stock images and public domain works), making it the safest choice for commercial projects where copyright concerns matter. Integration with Photoshop and Illustrator streamlines professional workflows.
- Commercially safe by design
- Seamless Creative Cloud integration
- Generative Fill/Expand features in Photoshop
- Pricing: Included with Creative Cloud subscriptions
Other Notable AI Art Generators
- Ideogram: Exceptional at rendering readable text within images a weakness for most AI generators
- Leonardo AI: Strong for game assets, concept art, and consistent character design
- NightCafe: User friendly interface with multiple AI models and an active community
- Canva AI: Best for non designers who need quick graphics integrated with design tools
- Flux: Emerging open source alternative with impressive quality, developed by Black Forest Labs (former Stable Diffusion researchers)
How to Create AI Art: A Practical Guide
Creating AI art is surprisingly accessible you can generate your first image in under five minutes. Here's a step by step guide for beginners.
Step 1: Choose Your Platform
For beginners, start with one of these user friendly options:
- ChatGPT: If you have a Plus subscription, just ask it to create an image
- Midjourney: Visit midjourney.com and create a free account to try it
- Canva: Use Magic Media within any Canva design
Step 2: Write an Effective Prompt
The prompt is your creative instruction to the AI. Better prompts lead to better results. A strong prompt typically includes:
- Subject: What's the main focus? ("a golden retriever," "a futuristic cityscape")
- Style: What aesthetic? ("oil painting," "photorealistic," "anime style," "watercolor")
- Mood/Atmosphere: What feeling? ("dramatic lighting," "peaceful," "dark and moody")
- Details: Specific elements ("wearing a red scarf," "at sunset," "surrounded by flowers")
- Technical specs: Quality markers ("highly detailed," "8K resolution," "cinematic")
Example Prompt: "A majestic snow leopard resting on a mountain cliff at golden hour, photorealistic style, dramatic lighting with sun rays breaking through clouds, highly detailed fur texture, 8K resolution, National Geographic photography style"
Step 3: Generate and Iterate
Your first result rarely matches your vision perfectly that's normal. Use these strategies to improve:
- Regenerate: Same prompt, different results. Generate multiple times to find the best version.
- Refine your prompt: Add specificity where the AI missed your intent. Remove elements that led to unwanted results.
- Use variations: Most tools let you create variations of a result you like.
- Upscale: Once satisfied, increase resolution for final use.

The Pros and Cons of AI Art
AI art isn't universally good or bad it's a powerful technology with significant benefits and legitimate concerns. Understanding both sides enables informed decisions about when and how to use it.

Advantages of AI Art
Democratization of Visual Creation: Anyone can now create compelling visuals regardless of artistic training. A small business owner can generate marketing graphics, a novelist can visualize characters, a teacher can create custom educational illustrations all without hiring an artist or learning complex software.
Unprecedented Speed and Iteration: What took hours or days now takes seconds. This enables rapid prototyping, quick exploration of creative directions, and the ability to test dozens of concepts before committing to one.
Overcoming Creative Blocks: Even professional artists use AI as a brainstorming tool. Generating variations on a concept can spark ideas that might never have emerged from staring at a blank canvas.
Cost Efficiency: For projects with limited budgets, AI art can provide visuals that would otherwise be unaffordable. This is particularly valuable for indie game developers, small publications, and content creators.
Disadvantages and Concerns
Impact on Human Artists: The most emotionally charged concern. AI can now produce in seconds what took artists years to learn. While some artists have adapted by incorporating AI into their workflows, others particularly those doing commercial illustration have seen work opportunities diminish.
Training Data Ethics: Most AI art models were trained on images scraped from the internet without explicit consent from creators. Many artists have found their distinctive styles replicated by AI systems trained on their work without credit, compensation, or permission.
Lack of "Soul": AI doesn't experience emotion, struggle with creative challenges, or imbue work with personal meaning. While outputs can be technically impressive, they lack the intentionality and human story that often gives art its deeper significance.
Current Technical Limitations: AI still struggles with consistent character design across images, accurate human anatomy (especially hands and teeth), readable text, and maintaining precise control over specific elements.
AI Art Ethics and Copyright: The Ongoing Debate
The legal and ethical questions surrounding AI art remain largely unresolved, with significant implications for artists, businesses, and the technology's future development.
Copyright: Who Owns AI Generated Art?
The U.S. Copyright Office has taken a clear position: purely AI generated images cannot be copyrighted because copyright requires human authorship. In several rulings (including the 2023 Zarya of the Dawn case and the 2024 Théâtre D'opéra Spatial appeal), the Office maintained that simply entering a prompt does not constitute sufficient creative contribution for copyright protection.
However, the situation is more nuanced when humans substantially modify AI outputs. Works combining AI generated elements with significant human creativity may receive partial protection for the human authored portions.
Training Data Lawsuits
Multiple class action lawsuits are currently challenging the legality of training AI models on copyrighted artwork without permission:
- Artists Sarah Andersen, Kelly McKernan, and Karla Ortiz filed suit against Stability AI, Midjourney, and DeviantArt in January 2023
- Getty Images sued Stability AI for allegedly training on millions of Getty's copyrighted photos
- A November 2023 lawsuit named over 4,700 artists whose work was allegedly used without consent
AI companies argue their training constitutes "fair use" a legal doctrine allowing limited use of copyrighted material for transformative purposes. Courts have yet to definitively rule on this question, making it one of the most consequential pending legal issues in technology.
Ethical Considerations for Users
Even without clear legal guidance, users face ethical decisions:
- Disclosure: Should AI generated art be labeled as such? Many believe transparency about AI use is essential, especially in professional or commercial contexts.
- Style Mimicry: Is it ethical to prompt AI to generate art "in the style of [living artist]"? Many argue this exploits artists' unique visual identities without compensation.
- Deception: Using AI to create fake photographs (like the viral Pope puffer jacket image) raises serious concerns about misinformation.
- Commercial Use: Profiting from AI art while artists whose work trained the system receive nothing troubles many observers.
The Future of AI Art: What's Next?
AI art technology continues advancing at a remarkable pace. Here are the key trends shaping its future:
Video Generation: Text to video models like Sora (OpenAI), Runway Gen 3, and Kling are making AI generated video increasingly viable. While not yet matching film quality, the gap is closing rapidly.
Real Time Generation: Tools like Krea AI now offer real time generation that updates as you type, enabling more intuitive creative workflows.
Multimodal AI: Systems that combine text, image, audio, and video understanding are enabling more sophisticated creative applications.
3D and Interactive Content: AI is beginning to generate 3D models, game assets, and interactive experiences not just static images.
Licensed and Ethical Training: Adobe Firefly's licensed content approach may become more common as legal pressures mount and businesses seek "safe" AI tools.
Frequently Asked Questions About AI Art
Is AI art "real" art?
This philosophical question has no definitive answer. AI art is undeniably visual output that can evoke emotional responses, convey ideas, and demonstrate aesthetic qualities. However, it lacks the intentional human expression traditionally considered central to art. Most perspectives acknowledge AI art as a new category distinct from but related to human created art.
Can I sell AI generated art?
Yes, in most cases, but with caveats. Most AI art platforms grant commercial usage rights to paid subscribers. However, you typically cannot copyright purely AI generated work, meaning others can legally copy it. For maximum protection, substantially modify AI outputs with your own creativity.
Which AI art generator is best for beginners?
ChatGPT (with Plus subscription) offers the gentlest learning curve just describe what you want in natural language. Canva's AI tools are also beginner friendly for those already using Canva. Midjourney offers beautiful results but requires learning its specific prompt syntax.
Will AI replace human artists?
AI will likely transform rather than eliminate artistic careers. Some commercial illustration work is already being affected, but demand remains strong for artists who can leverage AI tools effectively, maintain consistent brand/character work, provide unique creative vision, or create work with personal meaning and story.
Is using AI art cheating?
Context matters. Using AI art without disclosure when presenting it as your own hand made work is deceptive. Using AI as one tool among many in a creative workflow, especially with transparency about its role, is increasingly accepted. Ethics depend on intent, disclosure, and the specific use case.
Conclusion: Making Sense of the AI Art Revolution
AI art represents one of the most significant shifts in creative technology since the introduction of digital tools. It democratizes image creation, accelerates creative workflows, and opens possibilities that were science fiction just a decade ago.
Yet it also raises profound questions about creativity, authorship, and the value of human artistic expression. The ongoing legal battles, ethical debates, and industry disruption suggest we're still in the early chapters of this story.
For now, the most productive approach is informed engagement: understand the technology, recognize its capabilities and limitations, stay aware of the ethical dimensions, and make thoughtful choices about when and how to use it.
Whether AI art enhances or diminishes human creativity isn't predetermined, it depends on how we collectively choose to develop, regulate, and use these remarkable tools.